Hoarseness, or dysphonia, is a condition in which there is a change in one’s voice. There are many causes, but all result in an alteration of air-flow or in the ability of the vocal cord to vibrate normally. The larynx acts as an air-valve to regulate the amount of breath used to create speech. The vocal cords vibrate much like the strings of an instrument to create sound. The muscles of the larynx can vary the tension applied to the vocal cords to change pitch.
The muscles of the larynx can become weak or even paralyzed. These conditions typically result in a breathy voice because air passes though the larynx more quickly when the vocal cords do not come fully together in the midline.
Signs, Causes and Conditions
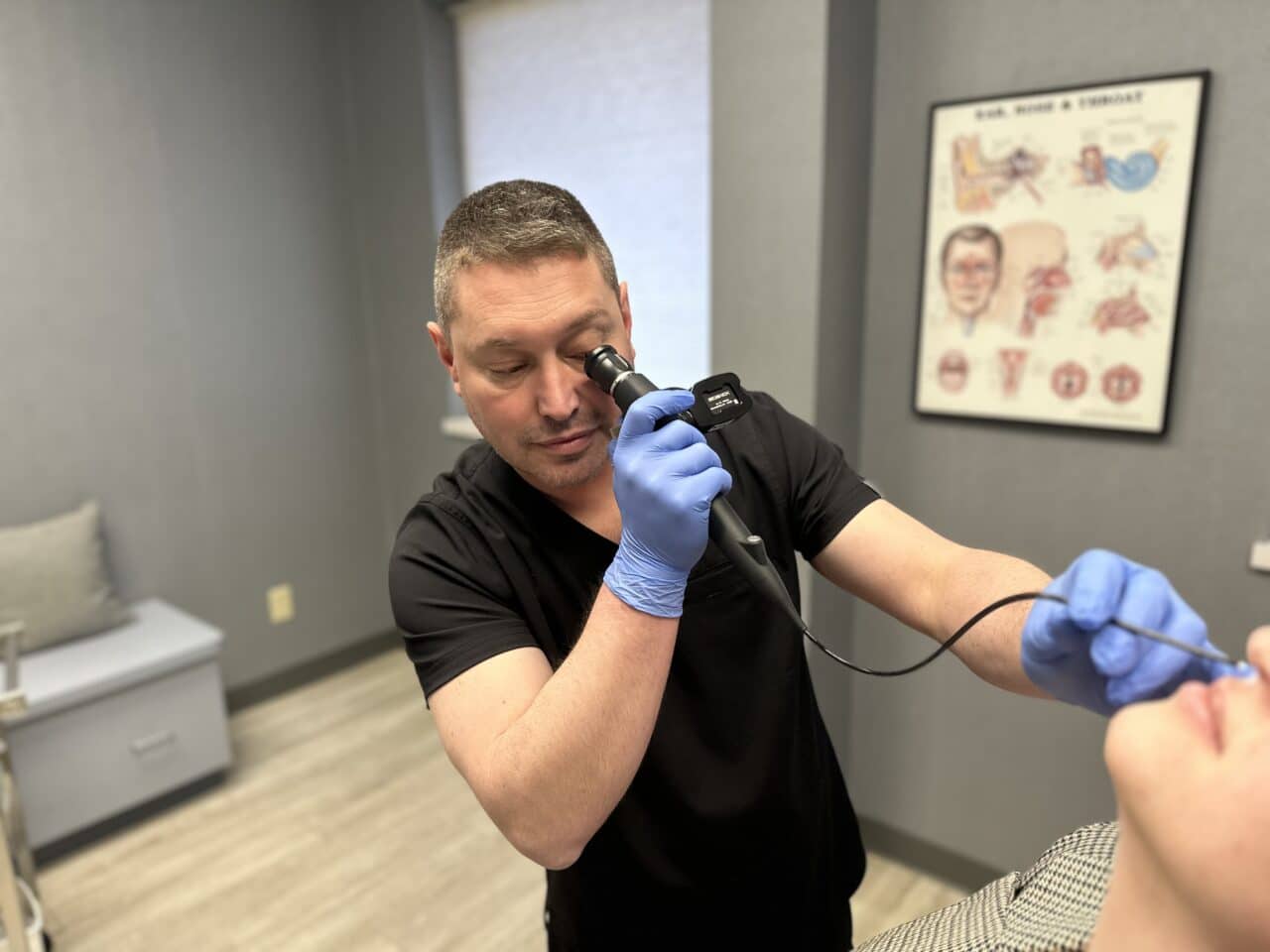
There are also numerous conditions which change the normal vibration patterns of the vocal cords and lead to hoarseness. In order to determine why a voice has become hoarse, it is necessary to actually look at the vocal cords. In some instances a simple mirror exam can allow your doctor to look at the vocal cords while looking through your mouth. More often, your doctor will uses a small, flexible fiberoptic scope that passes through the nose to look at the larynx from above. Some patients may need videostroboscopy which allows the movement of the vocal cords to be viewed in slow motion.
Common causes of hoarseness:
- Inflammation/laryngitis: this can be viral, bacterial, fungal, or related to smoking or acid reflux
- Benign Lesions: nodules, polyps, cysts, Reinke’s edema
- Cancerous lesion: squamous cell carcinoma in almost all cases
- Laryngeal injury from prior trauma or from intubation related to surgery
- Neuromuscular disorders: spasmodic dysphonia
Call Midwest ENT Centre at (636) 441-3100 for more information or to schedule an appointment.